Why Hormone Replacement Therapy Matters: Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) for women has been a controversial topic, often misunderstood due to misinterpretations of past studies like the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI). Over the last two decades, a clearer understanding has emerged, showing that appropriate HRT can dramatically improve quality of life for menopausal and perimenopausal women.
The WHI study—originally released in 2002—raised concerns about breast cancer, heart disease, and stroke. However, much of the data was misinterpreted, particularly concerning the differences between synthetic progestins and bioidentical hormones. Subsequent analysis revealed that the increased risks were primarily associated with synthetic progestins, not bioidentical progesterone or estradiol. Moreover, the benefits of HRT, including improved quality of life and reduced risks of osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease, often outweigh the potential risks when therapy is tailored appropriately.
Understanding Bioidentical vs. Synthetic Hormones Bioidentical hormones, such as estradiol and micronized progesterone, are chemically identical to the hormones naturally produced by the body. These hormones offer a safer and more physiologically compatible alternative to synthetic counterparts like conjugated equine estrogens (Premarin) and medroxyprogesterone acetate (Provera).
Why This Matters:
- Synthetic hormones used in the WHI study were linked to a slight increase in breast cancer risk. In contrast, bioidentical hormones have shown a lower risk profile in subsequent studies.
- Bioidentical hormones better mimic natural hormonal fluctuations, reducing side effects like mood swings and bloating.
As women progress through life, hormonal fluctuations are a natural part of aging, particularly during perimenopause and menopause. These changes involve a decline in key hormones—estradiol, progesterone, and testosterone—leading to various symptoms and health considerations.
The Transition: Perimenopause to Menopause
Perimenopause is a transitional phase that spans several years before menopause officially begins, typically occurring between the ages of 35 and 50. During this time, hormonal levels fluctuate unpredictably, leading to a variety of symptoms. Progesterone and testosterone levels often begin to decline in early perimenopause, resulting in irregular menstrual cycles, sleep disturbances, mood changes, and decreased libido. As estradiol levels start to drop more significantly in the later stages of perimenopause, symptoms like hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness may emerge.
This period is marked not only by vasomotor and urogenital changes but also by broader health concerns, such as reduced bone density and cardiovascular risks. Understanding and addressing these shifts is crucial to improving the quality of life and overall health during this transitional phase. Menopause is defined retrospectively as 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period, typically occurring between the ages of 45 and 55, with the average age being 51.
Symptoms of Hormonal Decline
Progesterone Decline:
- Sleep disturbances: Progesterone’s calming effect on the brain diminishes, leading to difficulty falling or staying asleep.
- Mood fluctuations: Anxiety and irritability may intensify without progesterone’s stabilizing influence.
- Irregular cycles: In perimenopause, falling progesterone levels contribute to menstrual irregularities, often with heavier or prolonged periods.
- Thinning hair: A decline in progesterone can contribute to hair thinning, as the hormone plays a role in counteracting the effects of androgens, which can weaken hair follicles.
Testosterone Decline:
- Decreased libido: Testosterone plays a critical role in sexual desire and arousal, and its decline can lead to reduced interest in intimacy.
- Reduced muscle mass and strength: Women may notice difficulty maintaining muscle tone and strength.
- Fatigue and low energy: Testosterone helps sustain energy levels, and its drop may exacerbate feelings of tiredness.
Estradiol Decline:
- Vasomotor symptoms: Hot flashes and night sweats are hallmark signs as estradiol levels drop, disrupting the hypothalamus’ ability to regulate body temperature.
- Urogenital symptoms: Vaginal dryness and atrophy, leading to discomfort and an increased risk of urinary infections.
Long-term risks: Reduced bone density, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures, as well as a heightened risk of cardiovascular disease due to loss of estrogen’s protective effects on the heart and blood vessels.
The Importance of Monitoring and Intervention
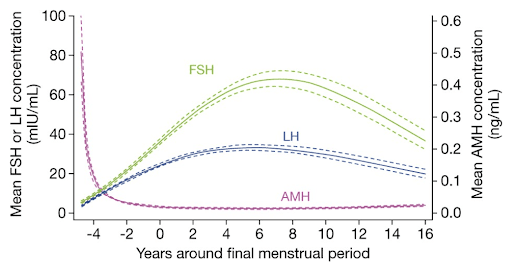
Understanding these hormonal shifts provides an opportunity for proactive management. Blood tests such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and estradiol levels can help determine where a woman is on the continuum from perimenopause to menopause. Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) testing may also provide insights into ovarian reserve, particularly for women exploring fertility options.
Key Treatments in HRT
- Estradiol:
- Benefits:
- Reduces vasomotor symptoms.
- Improves bone density and cardiovascular health.
- Alleviates vaginal atrophy.
- Risks:
- Slight risk of venous thromboembolism (lower with transdermal forms).
- Breast tenderness and headaches.
- Progesterone:
- Benefits:
- Prevents endometrial hyperplasia in women with a uterus.
- Improves sleep and mood.
- Risks:
- Mild dizziness or fatigue.
- Rare allergic reactions.
- Testosterone:
- Benefits:
- Enhances libido, energy, and muscle mass.
- Supports bone health and mental clarity.
- Risks:
- Acne and facial hair growth.
- Voice deepening at higher doses.
Tailoring HRT to Individual Needs HRT is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Providers must consider a woman’s symptoms, medical history, and personal preferences. Starting with the lowest effective dose and monitoring through regular blood tests ensures optimal outcomes.
Compounded BHRT: A Customized Approach Compounded BHRT allows for tailored formulations, such as Bi-est (estradiol and estriol). While not FDA-approved, these options offer personalized solutions when standard therapies are insufficient. Patients must work with reputable pharmacies to ensure quality and safety.
Take Control of Your Health Today:
HRT offers transformative benefits for women navigating menopause. By focusing on bioidentical hormones and individualized care, women can mitigate symptoms, protect long-term health, and enjoy a higher quality of life
The expert team at ReGen is here to help you regain balance, vitality, and confidence. Whether you’re navigating perimenopause, menopause, or simply seeking to optimize your wellness, we offer personalized Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy tailored to your unique needs.
Schedule your virtual or in-office consultation today with our compassionate and knowledgeable ReGen team. Together, we’ll create a plan to restore your energy, improve your quality of life, and help you feel like yourself again.
